madman
Super Moderator
This is going to be a common theme here!

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com
2. Hormone regimens for transgender men
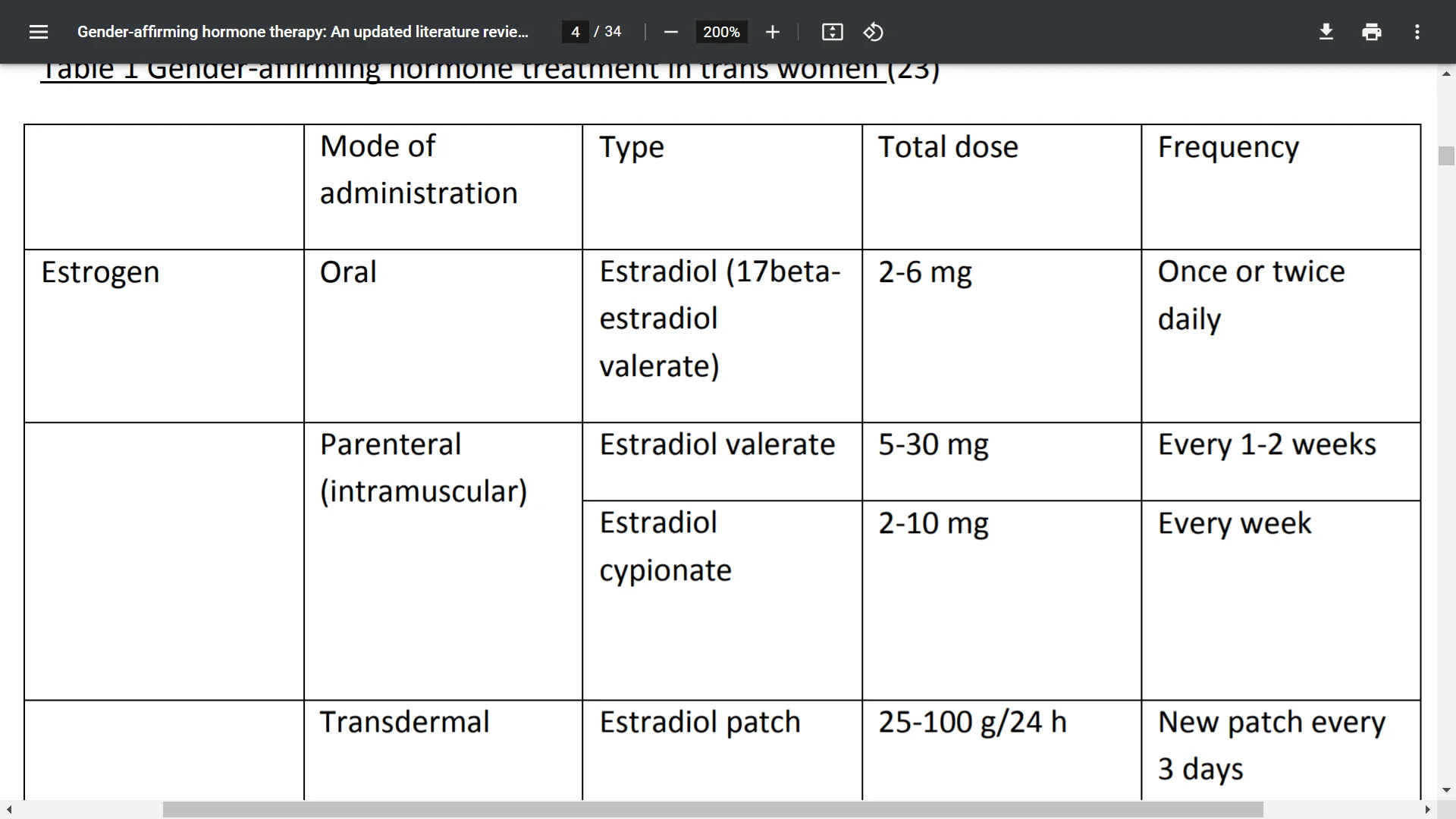
The primary goal of masculinizing HT is to stimulate physical changes consistent with the patient’s gender identity. Testosterone is the sole hormone administered. The aim is to achieve levels within the physiological range for cisgender men (300-1000ng/dL). There are several routes available to administer exogenous testosterone (Table 2). These include subcutaneous or intramuscular injections, transdermal gel or patches, and subcutaneous implants. With regards to achieving desired physiologic levels, no data support one route of administration over another, but higher testosterone levels are more easily achieved with parenteral treatment [5].
Injectable testosterone preparations include testosterone enanthate (TE), testosterone cypionate (TC), and testosterone undecanoate (TU). TE and TC can both be given as subcutaneous injections every week to ten days, or intramuscularly every two to three weeks. Typical doses for the weekly administration are 50 to 100mg [9]. These doses can be doubled and given with greater dosing intervals to reduce frequency of injections, although this is associated with greater fluctuation in levels [10]. With a longer carbon side chain, TU has a significantly longer half-life than TE and TC [11] [12], and can therefore be administered every 12 weeks [13]. Due to the fact that transgender men tend to be smaller in size than cisgender men, it may be advisable to begin with lower dosing and titrate upwards to avoid supraphysiologic levels.
Testosterone gels are typically given at doses of 50-100 mg/d, while transdermal patches are given at 2.5-7.5 mg/d [13]. Patients are advised to keep the application site clothed for 4 hours after administering gels to avoid skin-to-skin contact with others. Patients are also advised to avoid showering for 4 hours to ensure absorption [14]. Due to high levels of pruritus reported with use of patches, gels tend to be more commonly prescribed than patches'
Implantable testosterone pellets are also available, but titration will be more straightforward with shorter acting agents, leaving pellets reserved for maintenance [13]. Pellets contain 75mg of active ingredient and up to 6 can be inserted at once. Two pellets are typically inserted for every 25mg of parenteral testosterone required weekly and most patients require repeat implantation every 3 to 4 months.
2.1 Treatment effects
Although many transgender men desire maximum virilization, others may wish more modest results. Unfortunately for the latter, the impact of even low dose hormone therapy cannot be reliably predicted for any given individual and patients should be prepared for a range of results.
Within 3 to 6 months of initiating masculinizing therapy, transgender men can expect to experience amenorrhea, increased libido, coarsening of skin and acne, fat redistribution, increased muscle mass, and facial hair growth [15] [16] [17]. Over longer periods of time, patients can experience voice deepening and clitoromegaly [18] [19]. Male pattern hair loss can also occur due to the androgenic interaction with pilosebaceous hair follicles [20]. Some transgender men may welcome this change as it can be considered masculinizing, but some do not. Male pattern hair loss has been managed with 5alpha- reductase inhibitors, but patients should be counselled regarding reports of sexual function concerns, along with the lack of evidence for objective benefit in transgender men [21]. Height will not be affected by HT administered after puberty
For the majority of adult transgender men who began HT after puberty, a degree of nonreversible physical feminization will have occurred. Many transgender men will therefore be shorter, have a degree of female fat distribution [22], and have broader hips than cisgender men [23]. Patients can expect some degree of breast atrophy with long-term androgen therapy with studies showing histological changes [24] in breast tissue of transgender men with reduced glandular tissue and increased fibrous connective tissue comparable to changes seen in post-menopausal women [25] [26]

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com
 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com
 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com
 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com
 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com
 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com


 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com

 www.excelmale.com
www.excelmale.com
Endocrine treatment of transgender individuals - Excel Male TRT Forum
Endocrine treatment of transgender individuals: current guidelines and strategies Abstract Introduction: This review provides a summary of the medical and surgical care available to transgender individuals, as well as to offer proposals on how the medical field can progress to provide...
2. Hormone regimens for transgender men
The primary goal of masculinizing HT is to stimulate physical changes consistent with the patient’s gender identity. Testosterone is the sole hormone administered. The aim is to achieve levels within the physiological range for cisgender men (300-1000ng/dL). There are several routes available to administer exogenous testosterone (Table 2). These include subcutaneous or intramuscular injections, transdermal gel or patches, and subcutaneous implants. With regards to achieving desired physiologic levels, no data support one route of administration over another, but higher testosterone levels are more easily achieved with parenteral treatment [5].
Injectable testosterone preparations include testosterone enanthate (TE), testosterone cypionate (TC), and testosterone undecanoate (TU). TE and TC can both be given as subcutaneous injections every week to ten days, or intramuscularly every two to three weeks. Typical doses for the weekly administration are 50 to 100mg [9]. These doses can be doubled and given with greater dosing intervals to reduce frequency of injections, although this is associated with greater fluctuation in levels [10]. With a longer carbon side chain, TU has a significantly longer half-life than TE and TC [11] [12], and can therefore be administered every 12 weeks [13]. Due to the fact that transgender men tend to be smaller in size than cisgender men, it may be advisable to begin with lower dosing and titrate upwards to avoid supraphysiologic levels.
Testosterone gels are typically given at doses of 50-100 mg/d, while transdermal patches are given at 2.5-7.5 mg/d [13]. Patients are advised to keep the application site clothed for 4 hours after administering gels to avoid skin-to-skin contact with others. Patients are also advised to avoid showering for 4 hours to ensure absorption [14]. Due to high levels of pruritus reported with use of patches, gels tend to be more commonly prescribed than patches'
Implantable testosterone pellets are also available, but titration will be more straightforward with shorter acting agents, leaving pellets reserved for maintenance [13]. Pellets contain 75mg of active ingredient and up to 6 can be inserted at once. Two pellets are typically inserted for every 25mg of parenteral testosterone required weekly and most patients require repeat implantation every 3 to 4 months.
2.1 Treatment effects
Although many transgender men desire maximum virilization, others may wish more modest results. Unfortunately for the latter, the impact of even low dose hormone therapy cannot be reliably predicted for any given individual and patients should be prepared for a range of results.
Within 3 to 6 months of initiating masculinizing therapy, transgender men can expect to experience amenorrhea, increased libido, coarsening of skin and acne, fat redistribution, increased muscle mass, and facial hair growth [15] [16] [17]. Over longer periods of time, patients can experience voice deepening and clitoromegaly [18] [19]. Male pattern hair loss can also occur due to the androgenic interaction with pilosebaceous hair follicles [20]. Some transgender men may welcome this change as it can be considered masculinizing, but some do not. Male pattern hair loss has been managed with 5alpha- reductase inhibitors, but patients should be counselled regarding reports of sexual function concerns, along with the lack of evidence for objective benefit in transgender men [21]. Height will not be affected by HT administered after puberty
For the majority of adult transgender men who began HT after puberty, a degree of nonreversible physical feminization will have occurred. Many transgender men will therefore be shorter, have a degree of female fat distribution [22], and have broader hips than cisgender men [23]. Patients can expect some degree of breast atrophy with long-term androgen therapy with studies showing histological changes [24] in breast tissue of transgender men with reduced glandular tissue and increased fibrous connective tissue comparable to changes seen in post-menopausal women [25] [26]
Comparing Subcutaneous Testosterone to Intramuscular Testosterone in Gender Affirming Care of Transgender Male Adolescents - Excel Male TRT Forum
Comparing Subcutaneous Testosterone to Intramuscular Testosterone in Gender Affirming Care of Transgender Male Adolescents - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov Study Description Brief Summary: The trial studies the efficacy of subcutaneous (SQ) testosterone compared to intramuscular...
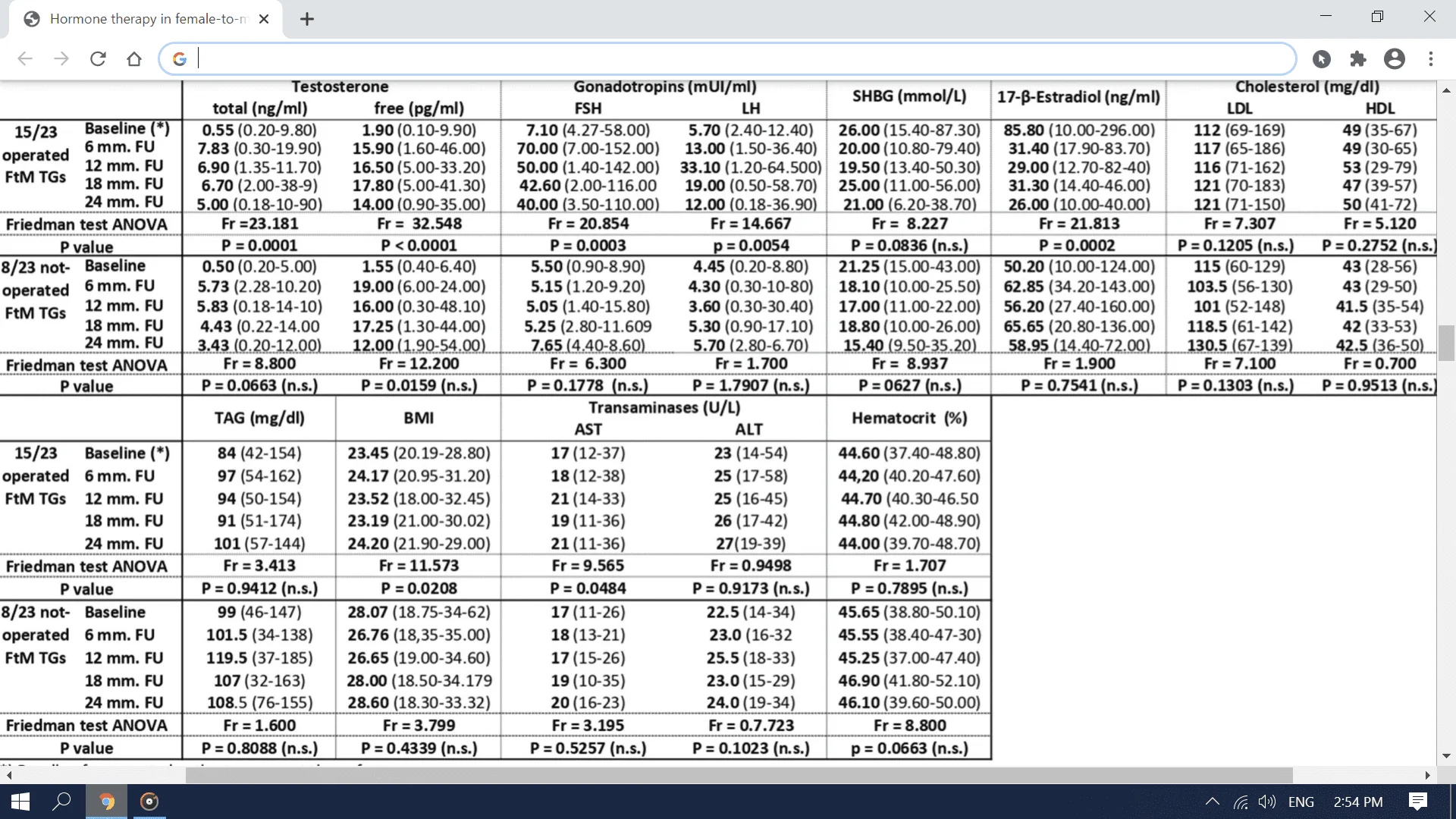
Hormone therapy of FTM transgender patients: searching for a lifelong balance
Abstract Background Reassignment of a female-to-male (FtM) person requires gender-affirming, the androgenic hormonal treatment that is planned to induce appropriate structural changes. This therapy must be prolonged long term, even after the sex reassignment surgery (SRS). The purpose of this...
Serum hormone concentrations in transgender people - Excel Male TRT Forum
SERUM HORMONE CONCENTRATIONS IN TRANSGENDER INDIVIDUALS RECEIVING GENDER AFFIRMING HORMONE THERAPY: A LONGITUDINAL RETROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY Objective: To examine the association of various gender affirmation hormone therapy (GAHT) regimens with blood hormone concentrations in transgender...
Transmen on TRT: Hormones Ranges
Reproductive Endocrinology Reference Intervals for Transgender Men on Stable Hormone Therapy Dina N. Greene, Robert L. Schmidt, Gabrielle Winston-McPherson, Jessica Rongitsch, Katherine L. Imborek, Jane A. Dickerson, Julia C. Drees, Robert M. Humble, Nicole Nisly, Nancy J. Dole, Susan K. Dane...
Serum Hormone Concentrations in Transgender Individuals Receiving GAHT - Excel Male TRT Forum
abstract Objective: To examine the association of various gender-affirming hormone therapy regimens with blood sex hormone concentrations in transgender individuals. Methods: This retrospective study included transgender people receiving gender-affirming hormone therapy between January 2000...
Physical and Psychological Effects of TRT in Tras Men Using IM-TE in Japanese TGM - Excel Male TRT Forum
ABSTRACT Introduction: The evidence on gender-affirming hormonal treatment (HT) for transgender persons is still insufficient. Aim: To characterize the physical and psychological effects of HT using testosterone enanthate in transgender men, and to validate the safety of this treatment...
Sub-q T Is Effective and Safe as GAHT in Transmasculine and Gender-Diverse Adolescents and Young Adults - Excel Male TRT Forum
Abstract Purpose: To describe our Center’s 8-year experience with subcutaneous testosterone (SC-T) as gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) in transmasculine and gender-diverse (TM/GD) youth. Methods: An Institutional Review Board (IRB)-approved retrospective study for 119 TM/GD subjects who...
Hormonal Gender Reassignment Treatment for Gender Dysphoria - Excel Male TRT Forum
Summary Background: No data are available at present on the prevalence of gender dysphoria (trans-identity) in Germany. On the basis of estimates from the Netherlands, it can be calculated that approximately 15 000 to 25 000 persons in Germany are affected. Persons suffering from gender...
Health Care for Transgender and Gender Diverse Individuals
ABSTRACT: An estimated 150,000 youth and 1.4 million adults living in the United States identify as transgender. This Committee Opinion offers guidance on providing inclusive and affirming care as well as clinical information on hormone therapy and preventive care; it also cites existing...
Clitorophallus modifications in transgender care - Excel Male TRT Forum
Abstract Background: The clitorophallus, or glans, is a critical structure in sexual development and plays an important role in how gender is conceptualized across the lifespan. This can be seen in both the evaluation and treatment of intersex individuals and the use of gender-affirming...
Gender Affirming Hormones in Youth - Excel Male TRT Forum
Abstract An increasing number of transgender and gender-expansive adolescents are seeking gender care at clinics and hospital programs and requesting gender-affirming hormonal treatment. Many are approved for this form of care to enhance their gender health. The interventions can either include...
Gender-affirming hormone therapy
Abstract In line with increasing numbers of transgender (trans) and gender non-binary people requesting hormone treatment, the body of available research is expanding. More clinical research groups are presenting data, and the number of participants in these studies is rising. Many previous...
Treating Acne in Transgender Persons Receiving Testosterone
Abstract Transgender persons who undergo masculinizing hormone therapy experience a wide array of dermatologic effects as they initiate and maintain testosterone therapy. Acne is one of the most common adverse effects for many transmasculine patients receiving testosterone. Acne can worsen...
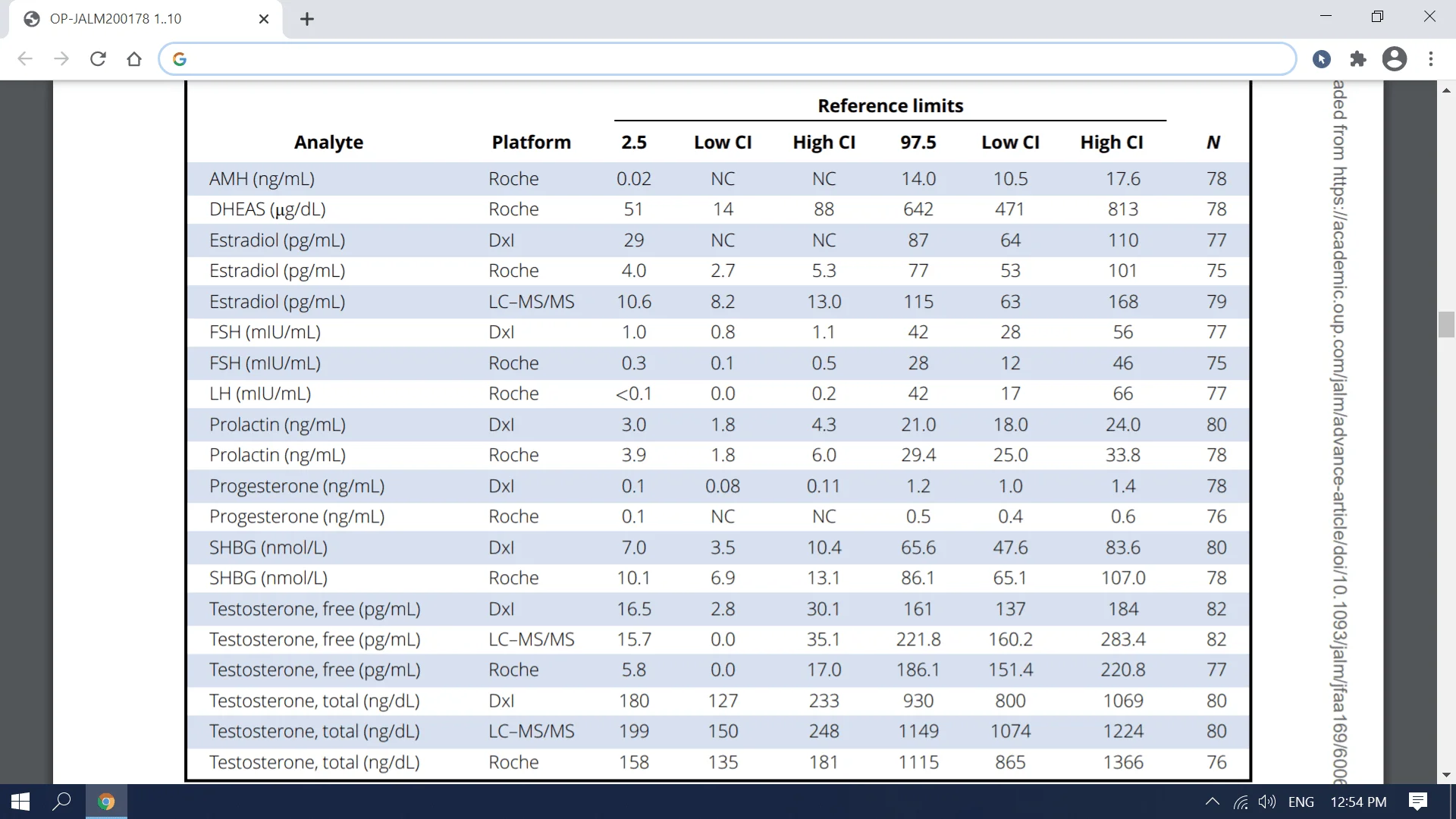
Transgender Clinical Chemistry Reference Intervals - Excel Male TRT Forum
Reference Intervals for Clinical Chemistry Analytes for Transgender Men and Women on Stable Hormone Therapy (2022) Robert M. Humble, Dina N. Greene, Robert L. Schmidt, Gabrielle Winston McPherson, Jessica Rongitsch, Katherine L. Imborek, Nicole Nisly, Nancy J. Dole, Susan K. Dane, Janice...
Endocrine Testing in Transgender Individuals - Excel Male TRT Forum
https://arup.utah.edu/education/straseski-inclusivity-2022.php Choosing the right laboratory test for any clinical situation can be difficult. One particularly complex situation is choosing appropriate testing for transgender and nonbinary patients. Gender and sex are words that many use...
The efficacy, safety, and outcomes of testosterone use among transgender men patients - Excel Male TRT Forum
The efficacy, safety, and outcomes of testosterone use among transgendermen patients: A review of the literature (2022) Rimel N. Mwamba | Adaora Ekwonu | Paulo V. B. Guimaraes | Omer A. Raheem Abstract Introduction: Gender dysphoria is the discrepancy between biological sex and gender...














