J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Feb;83(2):362-9.
Two-month treatment of obese subjects with the oral growth hormone (GH) secretagogue MK-677 increases GH secretion, fat-free mass, and energy expenditure.
Svensson J1, Lönn L, Jansson JO, Murphy G, Wyss D, Krupa D, Cerchio K, Polvino W, Gertz B, Boseaus I, Sjöström L, Bengtsson BA.
Abstract
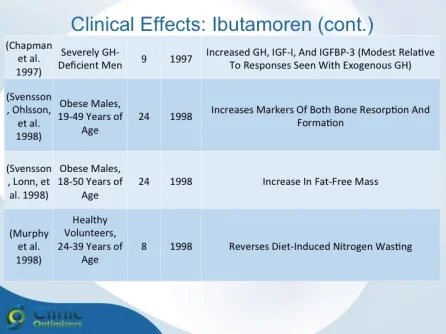
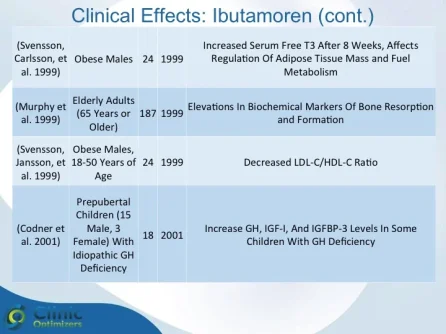
Obesity is associated with blunted GH secretion, unfavorable body composition, and increased cardiovascular mortality. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of oral treatment with the GH secretagogue MK-677 on GH secretion and body composition in otherwise healthy obese males. The study was randomized, double blind, parallel, and placebo controlled. Twenty-four obese males, aged 18-50 yr, with body mass indexes greater than 30 kg/m2 and waist/hip ratios greater than 0.95, were treated with MK-677 25 mg (n = 12) or placebo (n = 12) daily for 8 weeks. Serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) increased approximately 40% with MK-677 treatment (P < 0.001 vs. placebo). Serum IGF-binding protein-3 was also significantly increased (P < or = 0.001 vs. placebo). GH and PRL (peak and area under the curve values) were significantly increased after the initial dose of MK-677. Significant increases, with the exception of peak PRL, persisted at 2 and 8 weeks of treatment. The increases in GH and PRL after the initial dose were significantly greater than the increase seen after multiple doses. Serum and urinary concentrations of cortisol were not increased at 2 and 8 weeks (P = NS, vs. placebo). Fat-free mass increased significantly in the MK-677 treatment group when determined with dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (P < 0.01) or using a four-compartment model (P < 0.05). Total and visceral fat were not significantly changed with active therapy. The basal metabolic rate was significantly increased at 2 weeks of MK-677 treatment (P = 0.01) but not at 8 weeks (P = 0.1). Fasting concentrations of glucose and insulin were unchanged, whereas an oral glucose tolerance test showed impairment of glucose homeostasis at 2 and 8 weeks. We conclude that 2-month treatment with MK-677 in healthy obese males caused a sustained increase in serum levels of GH, IGF-I, and IGF-binding protein-3. The effects on cortisol secretion were transient. Changes in body composition and energy expenditure were of an anabolic nature, with a sustained increase in fat-free mass and a transient increase in basal metabolic rate. Further studies are needed to evaluate whether a higher dose of MK-677 or a more prolonged treatment period can promote a reduction in body fat.
For a list of studies and abstracts: Click here




FACT SHEET ATTACHED (FOR REGISTERED USERS)
Two-month treatment of obese subjects with the oral growth hormone (GH) secretagogue MK-677 increases GH secretion, fat-free mass, and energy expenditure.
Svensson J1, Lönn L, Jansson JO, Murphy G, Wyss D, Krupa D, Cerchio K, Polvino W, Gertz B, Boseaus I, Sjöström L, Bengtsson BA.
Abstract
Obesity is associated with blunted GH secretion, unfavorable body composition, and increased cardiovascular mortality. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of oral treatment with the GH secretagogue MK-677 on GH secretion and body composition in otherwise healthy obese males. The study was randomized, double blind, parallel, and placebo controlled. Twenty-four obese males, aged 18-50 yr, with body mass indexes greater than 30 kg/m2 and waist/hip ratios greater than 0.95, were treated with MK-677 25 mg (n = 12) or placebo (n = 12) daily for 8 weeks. Serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) increased approximately 40% with MK-677 treatment (P < 0.001 vs. placebo). Serum IGF-binding protein-3 was also significantly increased (P < or = 0.001 vs. placebo). GH and PRL (peak and area under the curve values) were significantly increased after the initial dose of MK-677. Significant increases, with the exception of peak PRL, persisted at 2 and 8 weeks of treatment. The increases in GH and PRL after the initial dose were significantly greater than the increase seen after multiple doses. Serum and urinary concentrations of cortisol were not increased at 2 and 8 weeks (P = NS, vs. placebo). Fat-free mass increased significantly in the MK-677 treatment group when determined with dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (P < 0.01) or using a four-compartment model (P < 0.05). Total and visceral fat were not significantly changed with active therapy. The basal metabolic rate was significantly increased at 2 weeks of MK-677 treatment (P = 0.01) but not at 8 weeks (P = 0.1). Fasting concentrations of glucose and insulin were unchanged, whereas an oral glucose tolerance test showed impairment of glucose homeostasis at 2 and 8 weeks. We conclude that 2-month treatment with MK-677 in healthy obese males caused a sustained increase in serum levels of GH, IGF-I, and IGF-binding protein-3. The effects on cortisol secretion were transient. Changes in body composition and energy expenditure were of an anabolic nature, with a sustained increase in fat-free mass and a transient increase in basal metabolic rate. Further studies are needed to evaluate whether a higher dose of MK-677 or a more prolonged treatment period can promote a reduction in body fat.
For a list of studies and abstracts: Click here

FACT SHEET ATTACHED (FOR REGISTERED USERS)
Last edited: