Nelson Vergel
Founder, ExcelMale.com
Old Drug: Chloroquine is a medication used to prevent and to treat malaria in areas where malaria is known to be sensitive to its effects.[1] Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication.[1] It is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash.[1] Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and low blood cell levels.[1] It appears to be safe for use during pregnancy.[1][2] Chloroquine is a member of the drug class 4-aminoquinoline.[1] It works against the asexual form of malaria inside the red blood cell.[1]
It is almost impossible to find chloroquine but this version can be found easily: Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil®) is a 4-amino-quinoline antimalarial medication that is widely used to treat systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and related inflammatory and dermatological conditions. It is a hydroxylated version of chloroquine, with a similar mechanism of action.

From:
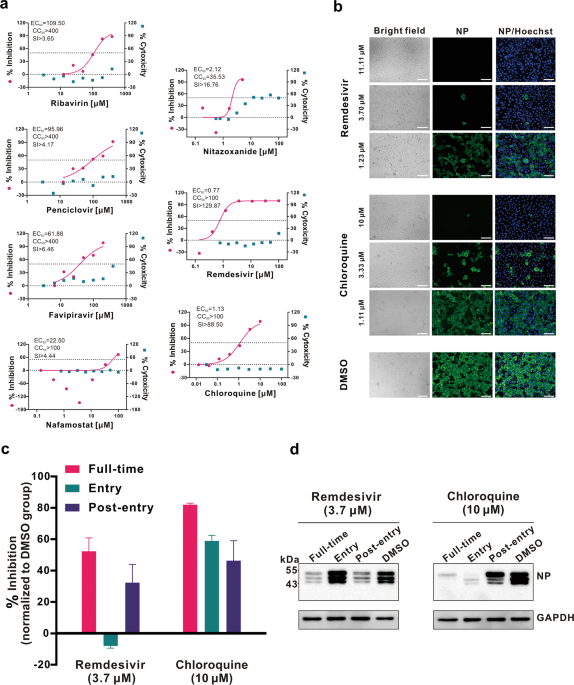
In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing ...
academic.oup.com › advance-article-pdf › doi › cid › ciaa237 › ciaa237
Zinc doses of 100 to 150 mg/day have been administered for certain patient groups for months with few adverse effects.2,10,35,36 Therefore, a zinc dose of some 80 mg/day for 1–2 weeks starting at the early symptoms of the common cold is unlikely to cause long-term adverse effects. Nevertheless, even though there is strong evidence that properly formulated zinc lozenges can shorten the duration of colds, the majority of zinc lozenges in the market seem to have either too low doses of zinc or they contain substances such as citric acid that bind zinc.8 Therefore, the findings of this study are not directly applicable to the wide variety of formulations of zinc lozenges on the market.
These are tablets of 50 mg: Zinc Supplement on Amazon
Zinc lozenges and the common cold: a meta-analysis comparing zinc acetate and zinc gluconate, and the role of zinc dosage

 selfhacked.com
selfhacked.com
I highly recommend watching this great video made by pulmonologist Dr. Seheult of https://www.medcram.com where he reviews current data on chloroquine plus zinc.
Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash.[1] Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and low blood cell levels.[1] It appears to be safe for use during pregnancy.[1][2] Chloroquine is a member of the drug class 4-aminoquinoline.[1] It works against the asexual form of malaria inside the red blood cell.[1]
It is almost impossible to find chloroquine but this version can be found easily: Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil®) is a 4-amino-quinoline antimalarial medication that is widely used to treat systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and related inflammatory and dermatological conditions. It is a hydroxylated version of chloroquine, with a similar mechanism of action.
From:
In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing ...
academic.oup.com › advance-article-pdf › doi › cid › ciaa237 › ciaa237
Zinc doses of 100 to 150 mg/day have been administered for certain patient groups for months with few adverse effects.2,10,35,36 Therefore, a zinc dose of some 80 mg/day for 1–2 weeks starting at the early symptoms of the common cold is unlikely to cause long-term adverse effects. Nevertheless, even though there is strong evidence that properly formulated zinc lozenges can shorten the duration of colds, the majority of zinc lozenges in the market seem to have either too low doses of zinc or they contain substances such as citric acid that bind zinc.8 Therefore, the findings of this study are not directly applicable to the wide variety of formulations of zinc lozenges on the market.
These are tablets of 50 mg: Zinc Supplement on Amazon
Zinc lozenges and the common cold: a meta-analysis comparing zinc acetate and zinc gluconate, and the role of zinc dosage

Can Zinc Help Fight Coronavirus (COVID-19)? - SelfHacked
Zinc supports immune health, but can it help with the new coronavirus? Get the latest science scoop here & find out if you should stock up.
I highly recommend watching this great video made by pulmonologist Dr. Seheult of https://www.medcram.com where he reviews current data on chloroquine plus zinc.
Last edited: