Nelson Vergel
Founder, ExcelMale.com
Clomiphene citrate and human chorionic gonadotropin are both effective in restoring testosterone in hypogonadism: a short‐course randomized study
Objectives
To compare serum testosterone response and symptom improvement in men with hypogonadism in response to treatment with clomiphene citrate (CC), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), or a combination of both therapies.
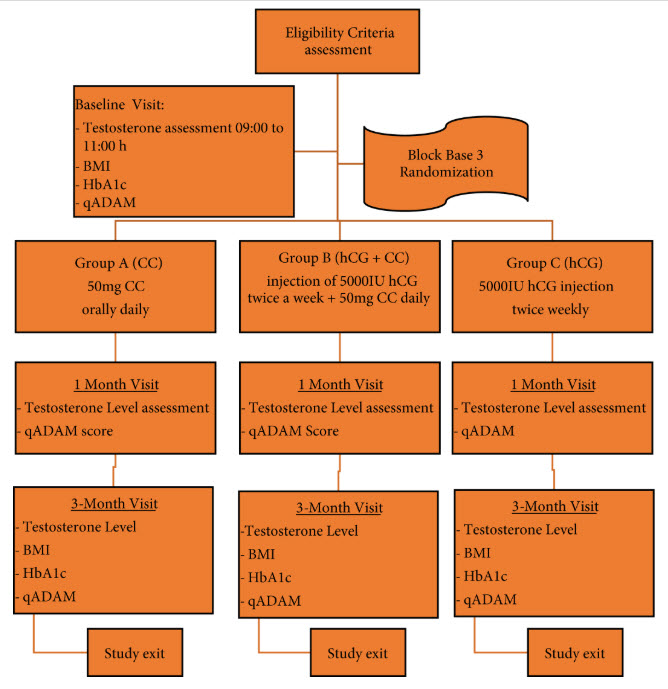
Patients and Methods
A total of 282 men with hypogonadism, wishing to preserve their fertility, were randomized to one of three treatment arms: CC 50 mg (n= 95); 5 000 IU hCG injections twice weekly (n = 94); or a combination of both therapies (CC + hCG; n = 94). All participants had complete medical history and had undergone thorough physical examination, including body mass index (BMI) assessment. Laboratory tests included serum total testosterone and glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) measurements. Quantitative Androgen Deficiency in the Aging Male (qADAM) questionnaire scores were also recorded. Morning samples of total serum testosterone levels were assessed at three time points: baseline, 1 and 3 months.
Results
Testosterone levels increased at 1 and 3 months in all three groups. The mean baseline testosterone level was 2.31 ± 0.66 nmol/L, BMI was 30.8 ± 6.2 kg/m2, and qADAM score was 20.5 ± 3.8 (50 means perfect quality of life and sexual function). Testosterone levels increased in all groups at all time points, with a final mean value of 5.17 ± 1.77 nmol/L (223% increase) with no statistically significant difference among the groups. qADAM scores had increased in all groups at 1 month (CC group: 6.36; hCG group: 5.08; CC + hCG group: 7.26) and at 3 months (CC group: 12.73; hCG group: 11.82; CC + hCG group: 15.13) with a significant difference in intergroup analysis for the CC + hCG group compared with the other two groups (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
All three treatments were equally effective in restoring testosterone levels. Single‐agent CC is simple, cheap and may be used as treatment for hypogonadism when maintenance of fertility is desired. This approach seems to be as effective as either hCG alone or a combination of hCG and CC.
Reference:
Habous, M. , Giona, S. , Tealab, A. , Aziz, M. , Williamson, B. , Nassar, M. , Abdelrahman, Z. , Remeah, A. , Abdelkader, M. , Binsaleh, S. and Muir, G. (2018), Clomiphene citrate and human chorionic gonadotropin are both effective in restoring testosterone in hypogonadism: a short‐course randomized study. BJU Int. . doi:10.1111/bju.14401
Objectives
To compare serum testosterone response and symptom improvement in men with hypogonadism in response to treatment with clomiphene citrate (CC), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), or a combination of both therapies.
Patients and Methods
A total of 282 men with hypogonadism, wishing to preserve their fertility, were randomized to one of three treatment arms: CC 50 mg (n= 95); 5 000 IU hCG injections twice weekly (n = 94); or a combination of both therapies (CC + hCG; n = 94). All participants had complete medical history and had undergone thorough physical examination, including body mass index (BMI) assessment. Laboratory tests included serum total testosterone and glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) measurements. Quantitative Androgen Deficiency in the Aging Male (qADAM) questionnaire scores were also recorded. Morning samples of total serum testosterone levels were assessed at three time points: baseline, 1 and 3 months.
Results
Testosterone levels increased at 1 and 3 months in all three groups. The mean baseline testosterone level was 2.31 ± 0.66 nmol/L, BMI was 30.8 ± 6.2 kg/m2, and qADAM score was 20.5 ± 3.8 (50 means perfect quality of life and sexual function). Testosterone levels increased in all groups at all time points, with a final mean value of 5.17 ± 1.77 nmol/L (223% increase) with no statistically significant difference among the groups. qADAM scores had increased in all groups at 1 month (CC group: 6.36; hCG group: 5.08; CC + hCG group: 7.26) and at 3 months (CC group: 12.73; hCG group: 11.82; CC + hCG group: 15.13) with a significant difference in intergroup analysis for the CC + hCG group compared with the other two groups (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
All three treatments were equally effective in restoring testosterone levels. Single‐agent CC is simple, cheap and may be used as treatment for hypogonadism when maintenance of fertility is desired. This approach seems to be as effective as either hCG alone or a combination of hCG and CC.
Reference:
Habous, M. , Giona, S. , Tealab, A. , Aziz, M. , Williamson, B. , Nassar, M. , Abdelrahman, Z. , Remeah, A. , Abdelkader, M. , Binsaleh, S. and Muir, G. (2018), Clomiphene citrate and human chorionic gonadotropin are both effective in restoring testosterone in hypogonadism: a short‐course randomized study. BJU Int. . doi:10.1111/bju.14401
Last edited:

















