Nelson Vergel
Founder, ExcelMale.com
Effects of Three Different Medications on Metabolic Parameters and Testicular Volume in Patients With Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
3-Year Experience
Clin Endocrinol. 2013;79(2):243-251.
Abstract
Introduction The aim of this study was to demonstrate the influences of three different treatment strategies on biochemical parameters and testicular volume (TV) in patients with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH).
Subjects design and methods Seventy-seven never-treated patients with IHH and age and body mass index (BMI)-matched 42 healthy controls were analysed in a retrospective design. Twenty-eight patients were treated with testosterone esters (TE), 25 patients were treated with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and 24 patients were treated with testosterone gel (TG). Biochemical parameters, tanner stages (TS) and TV were evaluated before and after 6 months of treatment.
Results Pretreatment TV, TS and biochemical test results were similar among the three treatment subgroup. In the TE-treated group, BMI, haemoglobin, haematocrit, creatinine, triglyceride, total testosterone (TT), TS and TV increased, but HDL-cholesterol (C) and urea level decreased significantly. In the hCG-treated group, triglyceride level decreased, and luteinizing hormone level, TS and TV increased significantly. BMI, TT, TS and TV increased, and leucocyte count, total-C, HDL-C levels decreased significantly in the TG-treated patients. No treatment type resulted in any changes in insulin resistance markers.
Conclusion hCG treatment resulted in favourable effects particularly on Testicular Volume and lipid parameters. When TV improvement is considered less important, TG treatment may be a better option for older patients with IHH because of its easy use, neutral effects on triglyceride, haemoglobin and haematocrit, and its beneficial effects on total cholesterol level.
Note: Dosing of hCG, injectable testosterone and testosterone gel were not "standard" as shown:
25 patients treated with hCG (Pregnyl® Organon hCG 5000 IU; Organon USA Inc., Roseland, NJ, USA) 5000 IU twice weekly, 28 patients treated with IM injections of oil-based blend of four esterized testosterone (TE) compounds (Sustanon® 250 mg Organon; Organon Schering-Plough Corporation, Istanbul, Turkey; 30 mg testosterone propionate, 60 mg testosterone phenylpropionate, 60 mg testosterone isocaproate and 100 mg testosterone decanoate) once every 3 weeks, and 24 patients treated with daily transdermal testosterone gel (TG; Testogel® Testosterone 50 mg/5 g-Schering, Schering Health Care Ltd, Burgess Hill, West Sussex) were enrolled.
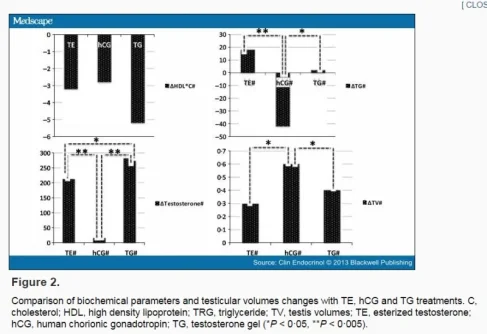
This graph shows the changes in HDL, triglycerides, testosterone, and testicular volume. It is surprising that 5000 IU of hCG twice per week hardly increased T levels. hCG looks good in all other parameters.

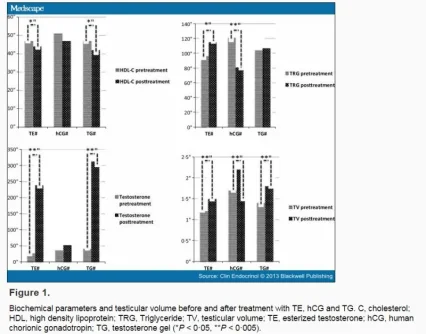
This graph shows the same parameters before and after each treatment option. You can see how all patients were undertreated (total T levels did not increase beyond 300 ng/dL)

The authors admit that their dosing regimen was not the best:
"Successful testosterone replacement treatment is guided by the hormone levels remaining above the lower limit of normal range just before the next application of drug.[SUP][16][/SUP] In this respect, we found only TG treatment achieved the target and hCG was the least effective. Similar to our result, IHH was previously found poorly responsive to hCG therapy in terms of normalization of serum testosterone.[SUP][17][/SUP]However, some other studies showed that serum testosterone increased to normal ranges after hCG treatment at a dose of 5000 IU.[SUP][18, 19][/SUP] Our subjects received 5000 IU hCG twice weekly. This regimen resulted in a significant increase in tanner scores, but the magnitude of change was lesser in comparison with the other two options. It is likely that serum testosterone increased to an effective level after hCG treatment, but this period remained relatively short, and testosterone level turned nearly to baseline values before the next injection time. Although some improvements were evident in tanner scores in this study, this treatment regimen may not optimal for obtaining basal testosterone level, also suggesting that smaller doses with shorter intervals may be more favourable. After injection of the commonly administered dose of 200 or 250 mg, TE has the disadvantage that it produces supraphysiological serum testosterone levels during the days immediately following administration, with a slow decline to the lower limit of normal within the following 10–14 days. Patients frequently dislike these swings in serum testosterone levels, which they experience as ups and downs in vigour, mood and sexual activity.[SUP][20][/SUP] Our study showed that serum testosterone falls to the levels lower than the normal just before the next injection. As a result, also for TE treatment, smaller doses with narrow intervals may be tried to reach physiological testosterone levels."
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/808683
3-Year Experience
Clin Endocrinol. 2013;79(2):243-251.
Abstract
Introduction The aim of this study was to demonstrate the influences of three different treatment strategies on biochemical parameters and testicular volume (TV) in patients with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH).
Subjects design and methods Seventy-seven never-treated patients with IHH and age and body mass index (BMI)-matched 42 healthy controls were analysed in a retrospective design. Twenty-eight patients were treated with testosterone esters (TE), 25 patients were treated with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and 24 patients were treated with testosterone gel (TG). Biochemical parameters, tanner stages (TS) and TV were evaluated before and after 6 months of treatment.
Results Pretreatment TV, TS and biochemical test results were similar among the three treatment subgroup. In the TE-treated group, BMI, haemoglobin, haematocrit, creatinine, triglyceride, total testosterone (TT), TS and TV increased, but HDL-cholesterol (C) and urea level decreased significantly. In the hCG-treated group, triglyceride level decreased, and luteinizing hormone level, TS and TV increased significantly. BMI, TT, TS and TV increased, and leucocyte count, total-C, HDL-C levels decreased significantly in the TG-treated patients. No treatment type resulted in any changes in insulin resistance markers.
Conclusion hCG treatment resulted in favourable effects particularly on Testicular Volume and lipid parameters. When TV improvement is considered less important, TG treatment may be a better option for older patients with IHH because of its easy use, neutral effects on triglyceride, haemoglobin and haematocrit, and its beneficial effects on total cholesterol level.
Note: Dosing of hCG, injectable testosterone and testosterone gel were not "standard" as shown:
25 patients treated with hCG (Pregnyl® Organon hCG 5000 IU; Organon USA Inc., Roseland, NJ, USA) 5000 IU twice weekly, 28 patients treated with IM injections of oil-based blend of four esterized testosterone (TE) compounds (Sustanon® 250 mg Organon; Organon Schering-Plough Corporation, Istanbul, Turkey; 30 mg testosterone propionate, 60 mg testosterone phenylpropionate, 60 mg testosterone isocaproate and 100 mg testosterone decanoate) once every 3 weeks, and 24 patients treated with daily transdermal testosterone gel (TG; Testogel® Testosterone 50 mg/5 g-Schering, Schering Health Care Ltd, Burgess Hill, West Sussex) were enrolled.
This graph shows the changes in HDL, triglycerides, testosterone, and testicular volume. It is surprising that 5000 IU of hCG twice per week hardly increased T levels. hCG looks good in all other parameters.
This graph shows the same parameters before and after each treatment option. You can see how all patients were undertreated (total T levels did not increase beyond 300 ng/dL)
The authors admit that their dosing regimen was not the best:
"Successful testosterone replacement treatment is guided by the hormone levels remaining above the lower limit of normal range just before the next application of drug.[SUP][16][/SUP] In this respect, we found only TG treatment achieved the target and hCG was the least effective. Similar to our result, IHH was previously found poorly responsive to hCG therapy in terms of normalization of serum testosterone.[SUP][17][/SUP]However, some other studies showed that serum testosterone increased to normal ranges after hCG treatment at a dose of 5000 IU.[SUP][18, 19][/SUP] Our subjects received 5000 IU hCG twice weekly. This regimen resulted in a significant increase in tanner scores, but the magnitude of change was lesser in comparison with the other two options. It is likely that serum testosterone increased to an effective level after hCG treatment, but this period remained relatively short, and testosterone level turned nearly to baseline values before the next injection time. Although some improvements were evident in tanner scores in this study, this treatment regimen may not optimal for obtaining basal testosterone level, also suggesting that smaller doses with shorter intervals may be more favourable. After injection of the commonly administered dose of 200 or 250 mg, TE has the disadvantage that it produces supraphysiological serum testosterone levels during the days immediately following administration, with a slow decline to the lower limit of normal within the following 10–14 days. Patients frequently dislike these swings in serum testosterone levels, which they experience as ups and downs in vigour, mood and sexual activity.[SUP][20][/SUP] Our study showed that serum testosterone falls to the levels lower than the normal just before the next injection. As a result, also for TE treatment, smaller doses with narrow intervals may be tried to reach physiological testosterone levels."
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/808683
Last edited:











