Nelson Vergel
Founder, ExcelMale.com
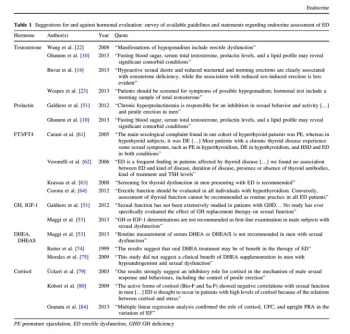
The following paper reviews most studies that have investigated the role of hormones on erectile function. The enclosed table shows the findings of these studies.
Endocrine evaluation of erectile dysfunction. Endocrine. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12020-014-0254-6
Erectile dysfunction is highly prevalent, affecting up to half of men in their 50-70s, and has been variably associated to a variety of causes including unhealthy lifestyles, such as smoking or overweight, or comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and neurological disorders. General interest toward ED has exploded since the introduction of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors-oral drugs that are widely accepted as the first line treatment in patients suffering from this conditions. In the last decade, the time lapse between first symptoms of sexual disorders and seeking of medical advice has greatly reduced. Unfortunately, none of the PDE5i has been proven curative, but rather acts as a symptomatic treatment. The availability of very active and safe drugs, however, diminished the space for diagnosis and search of etiological treatments. This is particularly true for the several endocrinopathies associated with ED. A number of epidemiological data support an inverse relationship between sexual health and testosterone levels, and it is well accepted that testosterone deficiency is a good marker of sexual and physical frailty. However, several other hormones, including LH, prolactin, TSH, and FT4 are involved in sexual functioning and should be investigated in a proper work-out of ED. Existing guidelines provide information almost entirely focusing on late-onset hypogonadism and therapeutic strategies; this mini-review aims to provide a wider spectrum of the diagnostic endocrine work-out of ED patients unrevealing the complexity of conditions, overt or subclinical, which can affect ED.

Endocrine evaluation of erectile dysfunction. Endocrine. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12020-014-0254-6
Erectile dysfunction is highly prevalent, affecting up to half of men in their 50-70s, and has been variably associated to a variety of causes including unhealthy lifestyles, such as smoking or overweight, or comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and neurological disorders. General interest toward ED has exploded since the introduction of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors-oral drugs that are widely accepted as the first line treatment in patients suffering from this conditions. In the last decade, the time lapse between first symptoms of sexual disorders and seeking of medical advice has greatly reduced. Unfortunately, none of the PDE5i has been proven curative, but rather acts as a symptomatic treatment. The availability of very active and safe drugs, however, diminished the space for diagnosis and search of etiological treatments. This is particularly true for the several endocrinopathies associated with ED. A number of epidemiological data support an inverse relationship between sexual health and testosterone levels, and it is well accepted that testosterone deficiency is a good marker of sexual and physical frailty. However, several other hormones, including LH, prolactin, TSH, and FT4 are involved in sexual functioning and should be investigated in a proper work-out of ED. Existing guidelines provide information almost entirely focusing on late-onset hypogonadism and therapeutic strategies; this mini-review aims to provide a wider spectrum of the diagnostic endocrine work-out of ED patients unrevealing the complexity of conditions, overt or subclinical, which can affect ED.